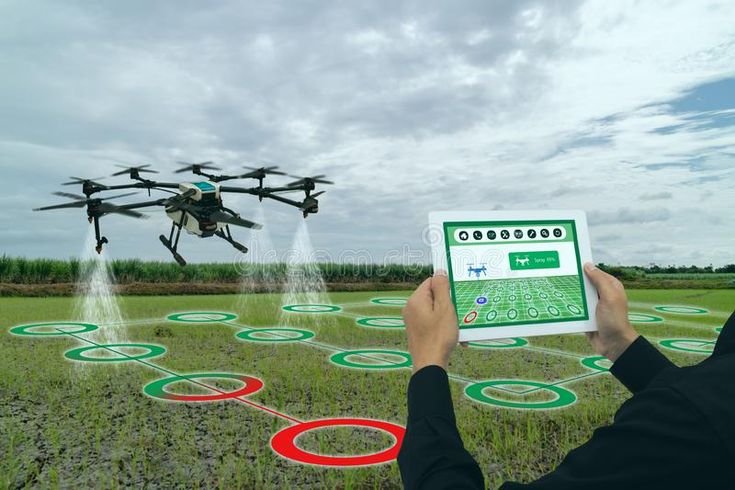
1. Greetings:
The integration of agricultural techniques with state-of-the-art technology is reshaping conventional farming in this age of efficiency and sustainability. This section explains what “smart agriculture” is and how it works, with an emphasis on how to enhance agricultural operations via the integration of IoT technology.
2. The Importance of Accuracy in Farming:
This part explores the growing worldwide need for food, the effects of warming temperatures, and the importance of precision farming techniques to guarantee effective and sustainable food production, shedding light on the difficulties encountered by traditional agriculture.
3. Smart Agriculture: To provide the groundwork for future comprehension, this section characterizes agriculture that is smart as the use of sophisticated technology, especially the Internet of Things (IoT), to automate, control, and monitor different parts of farming. The article delves into the ways these technologies may improve decision-making and farm management in general.
4. Major Elements of Intelligent Farming:
Smart agricultural systems rely on sensors, actuators, unmanned aircraft, autonomous equipment, data analytics, and more. In this section, we’ll go over the important components. It details the interplay between these components and how they come together to form a data-driven agricultural ecosystem.
5. The Internet of Things (IoT) and Its Role in Agriculture: In this part, we’ll look at the ways in which soil sensors, meteorological sensors, and devices for monitoring crop health all contribute to the provision of real-time data. With this information, farmers may optimize crop yields by making educated choices about the application of fertilizer, irrigation, and insect management.
6. Extending the scope to animals, this section delves into the ways in which the Internet of Things (IoT) is being used in precision livestock production. Smart feeding systems, wearable health monitors, and other monitoring equipment may improve cattle health and production.
7. Drone Technologies in Agriculture: This section delves into the usage of drones, specifically looking at how they may be used for precise spraying, aerial surveys, and crop monitoring. Farmers may evaluate crop health, spot problems, and optimize the distribution of resources with the use of drones, which provide a bird’s-eye perspective.
In Section 8, “Autonomous Machinery,” we look at how robotic harvesting machines, tractors, and drones may be used for precise work as part of the integration with autonomous equipment. These innovations allow for round-the-clock monitoring and operation, boost efficiency, and decrease the need for human labor.
9. Data Analytics & Decision Making Systems: With an emphasis on data analytics, this part delves into the processing and analysis of the massive volumes of data gathered by IoT devices. Through the use of decision support systems, farmers are able to maximize the use of resources and boost overall production by making choices based on data.
10. Smart agriculture practices foster sustainability by preventing the use of water, reducing chemical inputs, as well as optimizing energy consumption. This section addresses the negative environmental effects of agriculture and fosters eco-friendly farming.
11. Addressing the Challenges and alternatives of connection: This part recognizes the difficulties of connection in rural regions and explores creative alternatives, such as low-power wide-area networks and satellite communication, to guarantee extensive and dependable IoT connectivity within smart agriculture.
12. Financial Sustainability and Uptake: Looking at the financial side of things, this part investigates how much money farmers may make by using smart agricultural technology. It discusses the function of government programs and business alliances in encouraging broad adoption and possible obstacles to adoption.
13. Coming Soon: In this part, we will take a look at some of the new developments that are on the horizon, such as the use of AI, blockchain to make supply chains more transparent, and the possible influence of 5G technology on smart agriculture.
14. In conclusion, the integration of IoT technology into smart agriculture is revolutionizing conventional farming by making it more efficient, data-driven, and environmentally friendly. Connectivity but real-time data are the backbone of smart agriculture, which solves present problems and paves the way for precision farming in the future.
